The Development of Digital Comic as a Learning Media to Enhance Student's Understanding and Awareness on the Topic of Drugs
Abstract
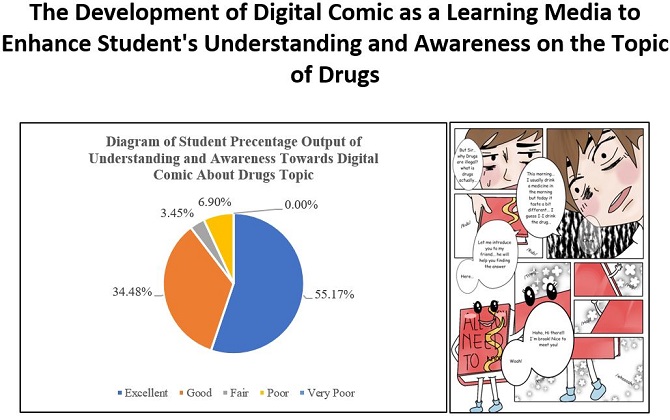
The human mindset significantly affects the progress of Science and Technology. Drugs are one of the examples that result from human complex thought. Lack of understanding of this topic can lead to others experimenting with dangerous psychotropic drugs. Studying sciences using only textbooks will not be imprinted in student memories. Consequently, incorporating media can help the teacher to improve student understanding. This study was aimed to facilitate students' understanding and awareness of the topic of drugs. The ADDIE model is a guideline for developing good media suitable for the topic. The resulting media was judged by an expert, a lecturer, and a teacher, who proceeded to use Index Aiken. The students' responses are gathered using a questionnaire of 20 statements and a Likert scale. The result shows that the lecturer's judgment rater agreement index has a V = 0.9625, indicating a high media score. At the same time, the teacher’s judgment has a V = 0.7875, which indicates an average score for the media. The students' responses show that 56.67% of students strongly agree that the comic can facilitate them to understand and be more aware of drugs. The findings show that lecturers and teachers agree that digital comics have the potential to be educational resources that foster comprehension and awareness and help students learn about drugs.
Keywords
Full Text:
Download PDFReferences
Budiman, H. (2017). Penggunaan media visual dalam proses pembelajaran [Use of visual media in the learning process]. Al-Tadzkiyyah: Jurnal Pendidikan Islam, 7(2), 171-182.
Chapin, N. (2003). Flowchart. In Encyclopedia of computer science (pp. 714-716).
Cheung, L. (2016). Using the ADDIE Model of Instructional Design to Teach Chest Radiograph Interpretation. Journal of Biomedical Education, 2016, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9502572
Eisner, E., & Powell, K. (2002). Special series on arts-based educational research: Art in science?. Curriculum Inquiry, 32(2), 131-159.
Fatimah, A. S., Santiana, S., & Saputra, Y. (2019). Digital Comic: An Innovation of Using Toondoo as Media Technology for Teaching English Short Story. English Review: Journal of English Education, 7(2), 101. https://doi.org/10.25134/erjee.v7i2.1526
Han, Y., Yan, W., Zheng, Y., Khan, M. Z., Yuan, K., & Lu, L. (2019). The rising crisis of illicit fentanyl use, overdose, and potential therapeutic strategies. Translational psychiatry, 9(1), 282. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0625-0
Handrianto, C., Jusoh, A. J., Goh, P. S. C., & Rashid, N. A. (2021). Using ADDIE model for designing instructional strategies to improve teaching competency of secondary schools teachers. Proceeding Webinar Konvensyen Kaunseling Kebangsaan Kali Ke, 22, 361-371.
Hidayatul, B., Mar'atus, S., & Sahal, H. (2019). Penggunaan Media Visual dalam Meningkatkan Minat Belajar Siswa. Universitas Muhammadiyah Sidoarjo.
Husna, A., & Fajar, D. M. (2022). Development of Interactive Learning Media Based on Articulate Storyline 3 on Newton’s Law Material with a Contextual Approach at the Junior High School Level. IJIS Edu : Indonesian Journal of Integrated Science Education, 4(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.29300/ijisedu.v4i1.5857
Jørgensen, S. E., & Halling-Sørensen, B. (2000). Drugs in the environment. Chemosphere, 40(7), 691-699.
Kaloeti, D. V. S., Manalu, R., Kristiana, I. F., & Bidzan, M. (2021). The Role of Social Media Use in Peer Bullying Victimization and Onset of Anxiety Among Indonesian Elementary School Children. Frontiers in Psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.635725
Kartina, A. A., Suciati, S. S., & Harlita, H. H. (2019). Analisis hasil ujian nasional materi zat aditif dan zat adiktif smp di surakarta [Analysis of the results of the national exam on additives and addictive substances for junior high schools in Surakarta]. In Prosiding SNPS (Seminar Nasional Pendidikan Sains) (pp. 162-167).
Levine, D. A. (2007). ‘Pharming’: the abuse of prescription and over-the-counter drugs in teens. Current opinion in pediatrics, 19(3), 270-274.
McNicol, S. (2017). The Potential of Educational Comics as a Health Information Medium. Health Information and Libraries Journal, 34(1), 20–31. https://doi.org/10.1111/hir.12145
Mims, M. (2022). Fresno County Sheriff’s Office 2020 Coroner Unit Statistics.
Nabil, N. R. A., Wulandari, I., Yamtinah, S., Ariani, S. R. D., & Ulfa, M. (2022). Analisis indeks Aiken untuk mengetahui validitas isi instrumen asesmen kompetensi minimum berbasis konteks sains kimia [Analysis of the Aiken index to determine the content validity of the chemical science context-based minimum competency assessment instrument]. Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan, 25(2), 184-191. https://doi.org/10.20961/paedagogia.v25i2.64566
O'Keeffe, G. S., & Clarke-Pearson, K. (2011). The impact of social media on children, adolescents, and families. Pediatrics, 127(4), 800-804. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-0054
Peterson, C. (2003). Bringing ADDIE to life: Instructional design at its best. Journal of Educational Multimedia and Hypermedia, 12(3), 227-241.
Porter, A. C., Smithson, J., Blank, R., & Zeidner, T. (2007). Alignment as a Teacher Variable. Applied Measurement in Education, 20(1), 27–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/08957340709336729
Priatna, B. A. (2008). Uji Coba Instrumen Penelitian dengan Menggunakan MS Excel dan SPSS. no. November, 1-22. http://file.upi.edu/Direktori/FPMIPA/JUR._PEND._MATEMATIKA/196412051990031-BAMBANG_AVIP_PRIATNA_M/Makalah_November_2008.pdf
Retnawati, H. (2016). Analisis kuantitatif instrumen penelitian (panduan peneliti, mahasiswa, dan psikometrian). Parama publishing.
Richey, R. C., & Klein, J. D. (2005). Developmental research methods: Creating knowledge from instructional design and development practice. Journal of Computing in higher Education, 16, 23-38.
Riyana, C. (2010). Komponen Pembelajaran. Online. http://kurtek. upi. edu/psb.
Rodríguez-Estrada, F. C., & Davis, L. S. (2015). Improving Visual Communication of Science Through the Incorporation of Graphic Design Theories and Practices Into Science Communication. Science Communication, 37(1), 140–148. https://doi.org/10.1177/1075547014562914
Ruiz-Colón, K., Chavez-Arias, C., Díaz-Alcalá, J. E., & Martínez, M. A. (2014). Xylazine intoxication in humans and its importance as an emerging adulterant in abused drugs: a comprehensive review of the literature. Forensic Science International, 240, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2014.03.015
Vassilikopoulou, M., Retalis, S., Nezi, M., & Boloudakis, M. (2011). Pilot use of digital educational comics in language teaching. Educational Media International, 48(2), 115-126. https://doi.org/10.1080/09523987.2011.576522
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17509/jsl.v7i2.61818
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2024 Haya Taira, Rika Rafikah Agustin, Diana Rochintaniawati

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


Jl. Dr. Setiabudhi 229 Bandung 40154, West Java, Indonesia










